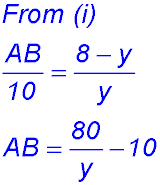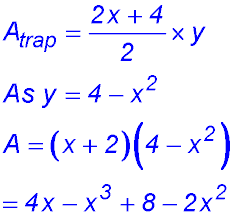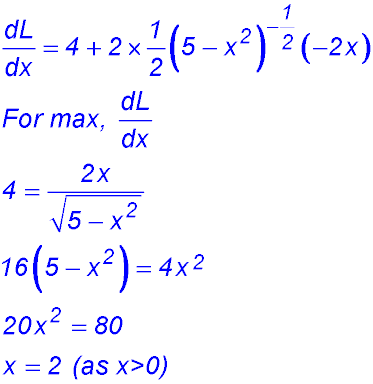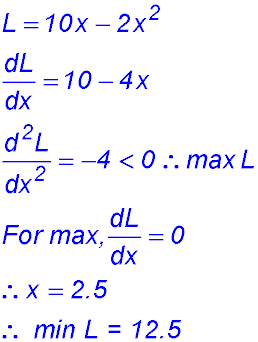Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Calculus - Differentiation - Applied max/mim questions.
Type 2: 2D shapes - Test Yourself 2 - Solutions.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
| Creating two shapes. |
1. (i) 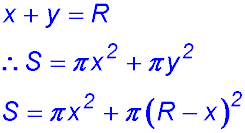
(iii) |
(ii) 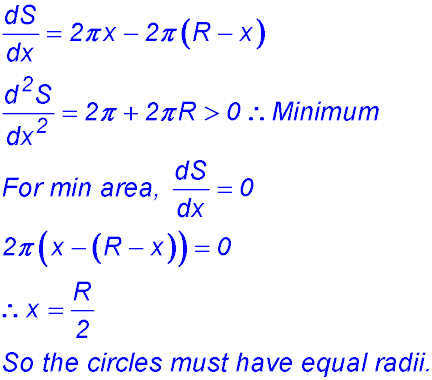 |
||||||||
2. (i) 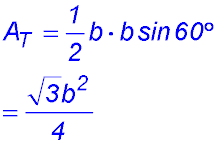
(ii) |
(iii) 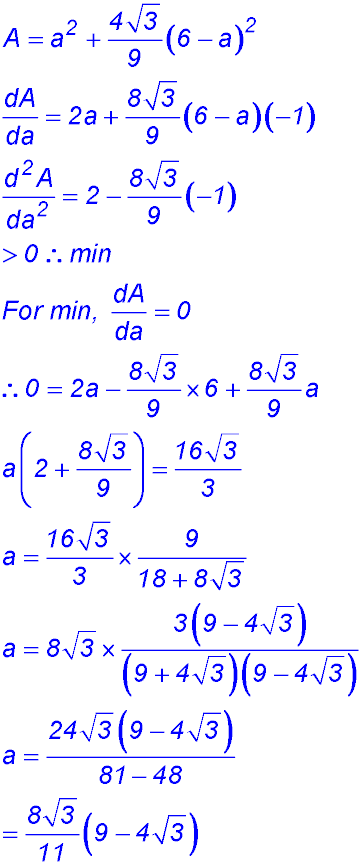 |
|||||||||
| Paddocks and areas. | 3. (i) PQ is simply the difference between the y values for the two curves - i.e. the vertical distance. So DPQ = (6x - x2) - (x2 - 4x) = 10x - 2x2. (ii) Area = (10x - 2x2)× x =10x2 - 2x3.
|
(iii) 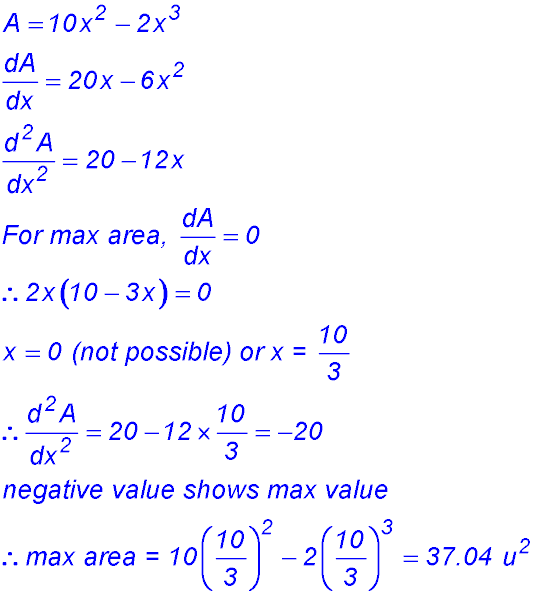 |
||||||||
4. 
(i) Perimeter 376 = 2(x + a + y + b).
(ii) Green Area = 6567 = xa + xb
|
(iii) If the vertical height is a maximum:
|
|||||||||
5. 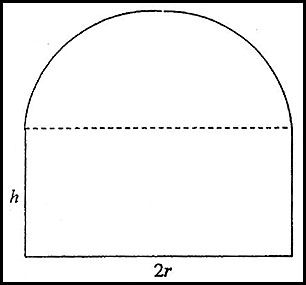
(i) The perimeter is P = 2h + 2r + circumference of the semicircle (of radius r).
|
(ii) 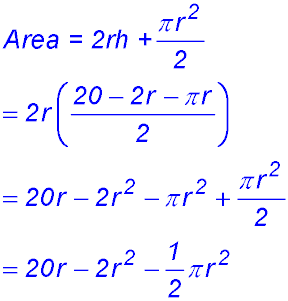
(iii)
|
|||||||||
| 6. (i) As the two areas are equal, the area of the big triangle ABC is twice the area of the smaller triangle AST.
(ii) 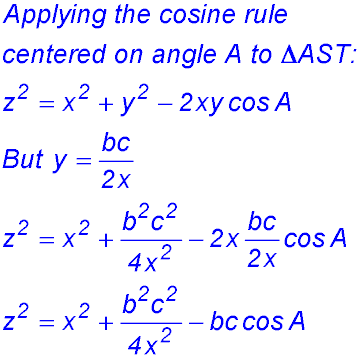 (iii) |
(iv) We need to find an expression for ST (= z) but the only expression we have has a cos A term. So we might have a hunch to try to eliminate the cos A and also use our result in (iii). So we could use the cosine rule again on the big triangle ABC:
|
|||||||||
| 7. | ||||||||||
8. (i) (ii) (iii) |
(iv)
Change of gradient from +ve to -ve hence a maximum area of 6√5 at x = √5. |
|||||||||
| Geometric shapes. |
9. 
(i)
(ii) |
(iii) 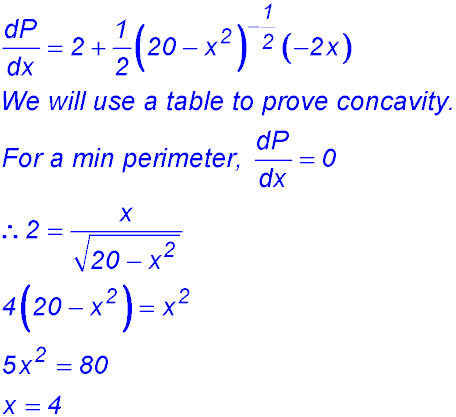
∴ change of concavity from -ve to +ve - so minimum. So the minimum perimeter is 14.47 m. |
||||||||
10. 
(ii) |
(iii) 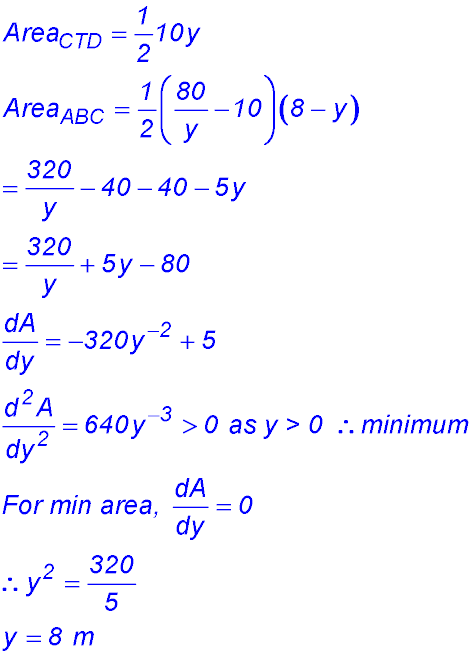 |
|||||||||
|
11. (i) R is (-2, 0) and S is (2, 0). (ii) RS = 4 and QP = 2x
|
(iii) 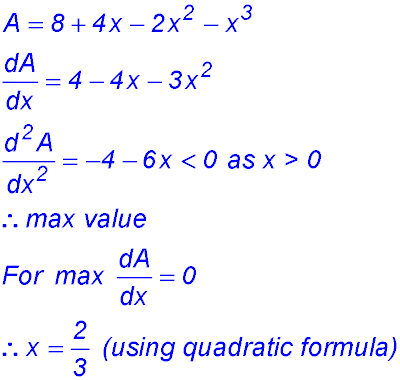 |
|||||||||
12. (i) 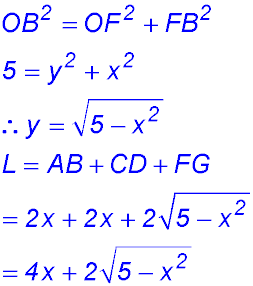 |
(ii)
Change of gradient from +ve to -ve - so maximum length when x = 2. |
|||||||||
| 13. Draw verticals from C and D to AB. Join OC.
AE = FB = x - so EF = DC = 2R - 2x. OC = R.
|
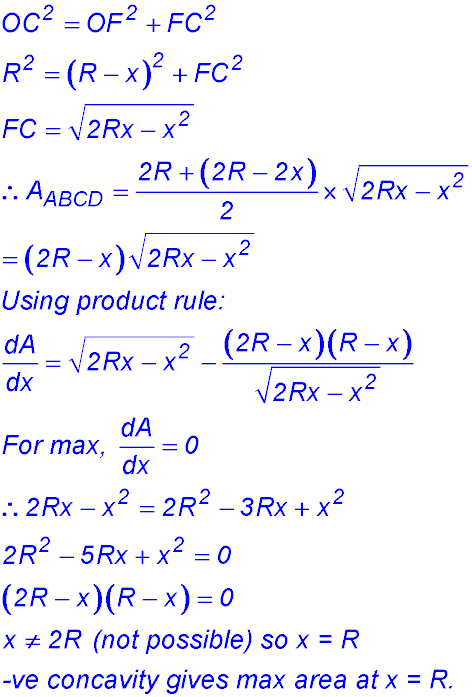 |
|||||||||
| Distance between 2 curves. | 14. (i)
|
(ii) PQ = L = x(6 - x) - x(x - 4)
(iii) |
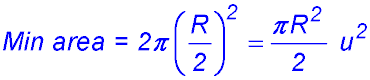
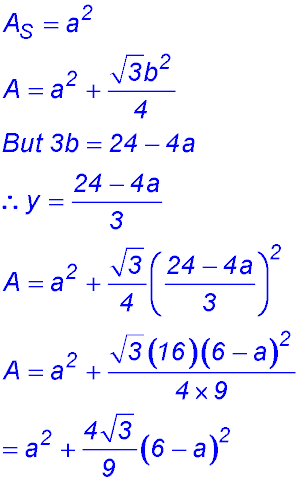


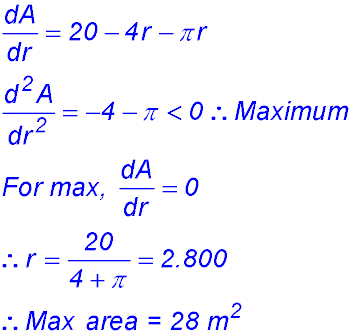
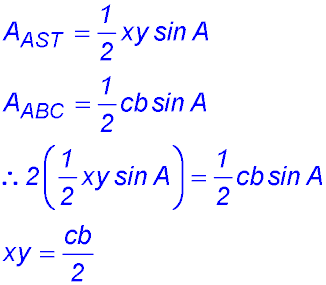
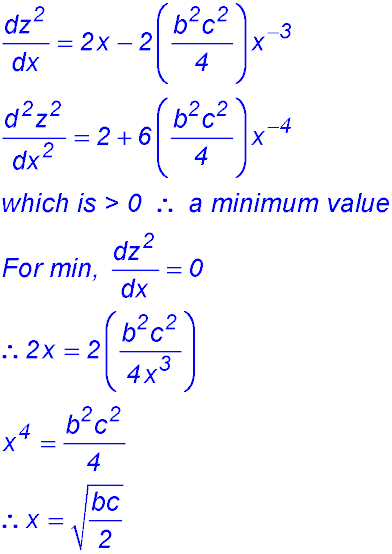
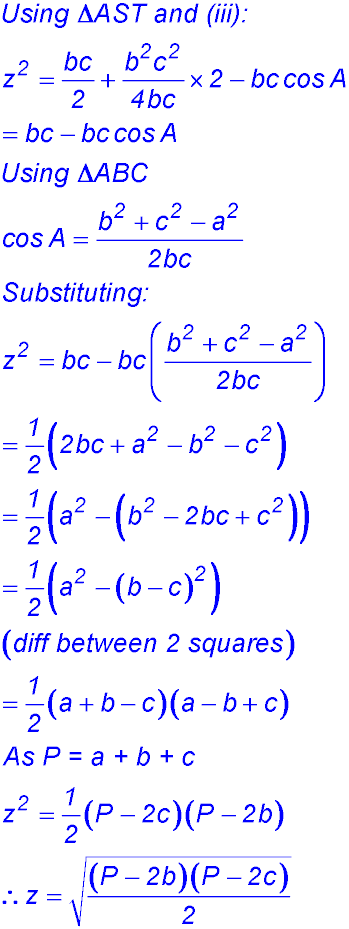
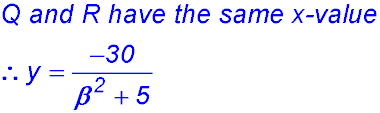
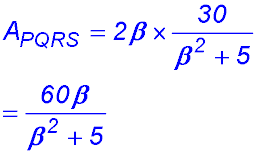
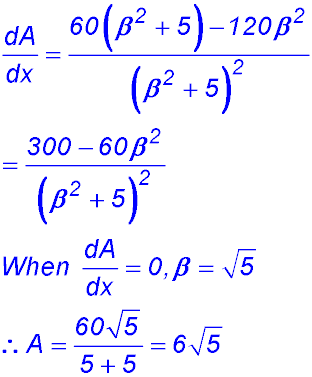
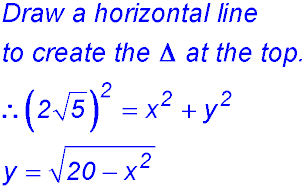
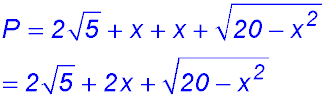 .
.